Calculating 2025 EV Total Cost of Ownership: 25% Lower Than Gasoline Cars
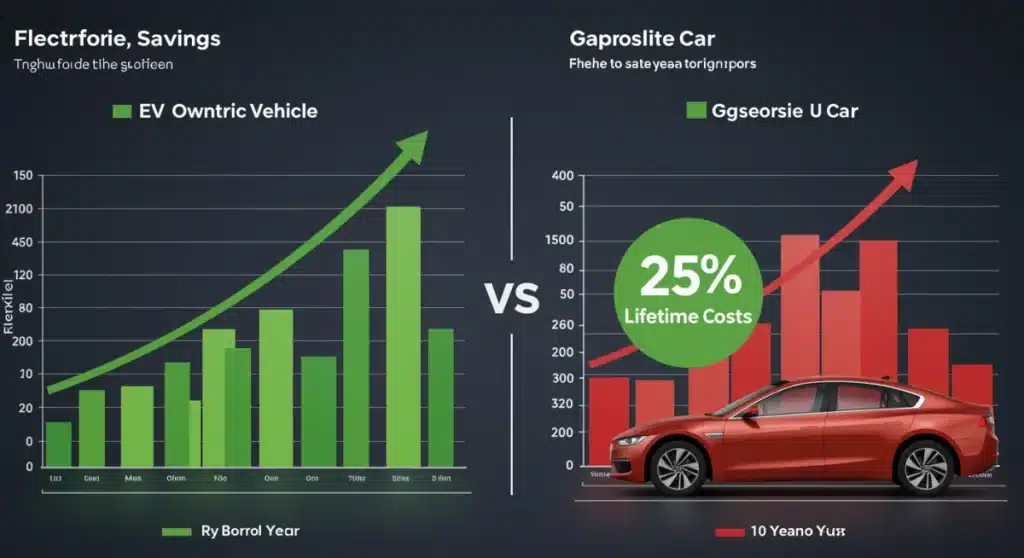
Calculating your 2025 EV total cost of ownership reveals a 25% lower lifetime expense compared to gasoline cars, driven by fuel, maintenance, and incentives.
Recent projections confirm that Calculating Your 2025 EV Total Cost of Ownership: Expect 25% Lower Lifetime Costs Than Gasoline Cars (FINANCIAL IMPACT) will reveal significant financial advantages for consumers. This pivotal shift is driven by evolving market dynamics, technological advancements, and sustained policy support, making electric vehicles an increasingly compelling economic choice.
The Shifting Landscape of Automotive Economics
The financial calculus for vehicle ownership is undergoing a profound transformation. Historically, the upfront cost of electric vehicles (EVs) presented a barrier, often overshadowing their long-term operational savings. However, as of late 2024, industry analyses and consumer data indicate a clear trajectory where the total cost of ownership (TCO) for EVs is not only competitive but demonstrably lower than that of comparable gasoline-powered cars.
This evolving landscape is influenced by several converging factors, including declining battery production costs, increased manufacturing efficiencies, and a robust expansion of charging infrastructure. These elements collectively contribute to a more attractive economic proposition for prospective EV buyers, pushing the narrative beyond environmental benefits to tangible financial gains.
Key Drivers of EV Cost Reduction
- Battery Price Decreases: Continuous advancements in battery technology and scaled production are driving down the most expensive component of an EV.
- Government Incentives: Federal, state, and local incentives for EV purchases and charging infrastructure remain significant, reducing initial outlay.
- Increased Competition: A growing number of manufacturers entering the EV market is fostering competitive pricing and diverse model options.
Fueling Savings: Electricity vs. Gasoline Prices
One of the most immediate and impactful areas where EVs outshine gasoline cars in TCO is fuel costs. Electricity, on average, is significantly cheaper per mile than gasoline, a trend that is expected to continue into 2025. This disparity becomes even more pronounced when considering the efficiency of electric powertrains compared to internal combustion engines.
While gasoline prices are subject to geopolitical volatility and supply chain disruptions, electricity rates tend to be more stable, particularly for residential charging during off-peak hours. This predictability in ‘fueling’ costs provides EV owners with a greater sense of financial security and allows for more accurate budgeting over the vehicle’s lifetime.
Charging Infrastructure and Cost Efficiency
The expansion of home and public charging options further enhances cost efficiency. Many EV owners can take advantage of lower utility rates by charging their vehicles overnight, effectively turning their garage into a personal, low-cost filling station. Public fast-charging networks, while sometimes more expensive than home charging, still often provide a cost advantage over gasoline, especially for long-distance travel.
- Home Charging Convenience: The ability to charge at home, often overnight, leverages lower electricity rates.
- Public Charging Network Growth: Increasing availability of public charging, though variable in cost, still offers savings.
- Energy Efficiency: EVs convert a much higher percentage of their energy into motion compared to gasoline cars, reducing overall energy consumption.
Maintenance Matters: Fewer Moving Parts, Lower Bills
The inherent simplicity of an electric powertrain translates directly into lower maintenance costs. Unlike gasoline engines with their multitude of moving parts, fluids, and complex exhaust systems, EVs have fewer components that require regular servicing or replacement. This structural advantage contributes significantly to the projected 25% lower lifetime costs.
Traditional gasoline cars demand routine oil changes, spark plug replacements, belt inspections, and complex emissions system maintenance. EVs, by contrast, eliminate most of these requirements. Their regenerative braking systems also extend the life of brake pads, further reducing wear and tear expenses over the vehicle’s lifespan.
The cumulative effect of these reduced maintenance needs results in substantial savings for EV owners. While specific figures can vary based on model and driving habits, the general consensus among automotive experts and repair shops points to a clear financial benefit for electric vehicle owners.
Reduced Component Wear
Electric motors are renowned for their durability and require minimal upkeep compared to internal combustion engines. This translates to fewer trips to the mechanic and lower bills for parts and labor. The absence of an exhaust system means no catalytic converter issues or muffler replacements, common and costly repairs for gasoline vehicles.
Government Incentives and Tax Credits in 2025
Government incentives continue to play a crucial role in lowering the effective purchase price and overall TCO for electric vehicles in 2025. Both federal and state-level programs aim to accelerate EV adoption by making them more financially accessible to a wider range of consumers. These incentives can take various forms, including direct tax credits, rebates, and grants for charging infrastructure.
The specific details of these programs can evolve, but the overarching commitment to supporting EV growth remains strong. Prospective buyers are advised to research current incentives applicable to their region and chosen EV model, as these can significantly impact the initial investment and, consequently, the lifetime cost equation.
Navigating Available Programs
- Federal Tax Credits: Eligibility for federal tax credits, often up to $7,500, depends on vehicle manufacturing origin, battery component sourcing, and the buyer’s income.
- State and Local Rebates: Many states and municipalities offer additional rebates, often stacking with federal incentives, further reducing the purchase price.
- Charging Infrastructure Grants: Programs exist to help offset the cost of installing home charging stations, another factor in overall TCO.
Resale Value and Depreciation: A New Dynamic
The resale value of electric vehicles is an increasingly important factor when calculating your 2025 EV total cost of ownership. While early EVs sometimes faced steeper depreciation curves, the market has matured significantly. As battery technology improves and public perception shifts, the depreciation rates for EVs are beginning to align more closely with, and in some cases even outperform, those of comparable gasoline vehicles.
Factors influencing EV resale value include battery health, range, demand for used EVs, and the pace of new technological introductions. As the charging infrastructure expands and battery longevity proves reliable, the used EV market is expected to strengthen, providing better retention of value for owners.
Analysts are closely monitoring the used EV market, and current trends suggest that well-maintained EVs with good range and contemporary features will hold their value effectively. This improved resale potential contributes positively to the overall lifetime financial assessment.
Market Maturation and Future Projections
The increasing acceptance of EVs, coupled with advancements in battery technology that extend vehicle life and performance, is bolstering their long-term value. As more consumers become comfortable with electric drivetrains, demand in the secondary market is expected to remain robust.
The Environmental and Economic Synergy
Beyond the direct financial savings of calculating your 2025 EV total cost of ownership, there’s a powerful synergy between environmental responsibility and economic benefit. Reducing reliance on fossil fuels not only lessens carbon emissions but also insulates consumers from volatile gas prices, offering a more stable and predictable financial outlay for transportation.
The transition to EVs supports broader sustainability goals, contributing to cleaner air and reduced urban noise pollution. These societal benefits, while not directly quantifiable in a personal TCO calculation, contribute to a higher quality of life and potentially lower healthcare costs in the long run. The economic incentives align with these environmental objectives, creating a compelling case for widespread adoption.
This dual benefit—financial savings coupled with environmental stewardship—positions EVs as a smart choice for both individual consumers and the planet. The ongoing policy support and technological innovation further solidify this synergy, promising continued benefits into the future.
Long-term Societal Benefits
- Reduced Urban Pollution: EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air in cities.
- Energy Independence: Shifting from imported oil to domestically generated electricity enhances national energy security.
- Innovation and Job Growth: The burgeoning EV industry fosters technological innovation and creates new jobs in manufacturing, charging infrastructure, and related services.
| Key Financial Aspect | EV vs. Gasoline Car (2025 Projections) |
|---|---|
| Overall Lifetime Cost | EVs projected 25% lower than comparable gasoline cars. |
| Fuel Expenses | Significantly lower for EVs due to cheaper electricity and higher efficiency. |
| Maintenance Costs | Reduced for EVs due to fewer moving parts and regenerative braking. |
| Government Incentives | Federal and state tax credits/rebates continue to lower initial EV purchase costs. |
Frequently Asked Questions About EV Ownership Costs
The primary factors include significantly lower fuel costs (electricity vs. gasoline), reduced maintenance due to fewer moving parts, and ongoing government incentives like tax credits and rebates that lower the initial purchase price.
While often higher than comparable gasoline cars, upfront EV prices are decreasing. When combined with federal and state incentives, the net purchase cost becomes much more competitive, making the long-term TCO more attractive.
EVs have fewer components requiring regular maintenance, such as oil changes, spark plugs, and exhaust systems. Regenerative braking also extends brake pad life, leading to substantially lower maintenance expenses over the vehicle’s lifespan.
Yes, federal and various state incentives are expected to continue into 2025, though specific eligibility criteria and amounts may adjust. These programs remain crucial for encouraging EV adoption and reducing consumer costs.
Battery technology has advanced considerably, with warranties typically covering 8-10 years or 100,000-150,000 miles. Most EV batteries outlast this, and replacement costs are decreasing, making it less of a concern for TCO for the average owner.
What This Means
The projected 25% lower lifetime costs for electric vehicles by 2025 represents a critical inflection point in the automotive industry. This isn’t merely an incremental improvement; it signals a fundamental shift in economic viability that will accelerate EV adoption. Consumers are increasingly prioritizing financial prudence, and these projections provide a compelling reason to consider an electric vehicle. Expect automakers to further emphasize TCO in their marketing, and for policy discussions to continue focusing on infrastructure and incentive stability to cement this financial advantage for EV owners.





