2025 Federal Fuel Efficiency Standards: What’s the Latest?

The latest on the 2025 federal fuel efficiency standards indicates a complex interplay between ambitious environmental goals, technological advancements in the automotive industry, and economic considerations impacting both manufacturers and consumers.
For decades, federal fuel efficiency standards have shaped the automotive landscape, pushing innovation and defining the capabilities of the vehicles we drive. As we approach 2025, the question of What’s the Latest on the 2025 Federal Fuel Efficiency Standards? is more pertinent than ever, carrying significant implications for car manufacturers, consumers, and the broader environmental agenda. Understanding these evolving regulations is crucial to grasping the future direction of the auto industry.
The Evolution of Fuel Efficiency Standards in the US
The history of fuel efficiency standards in the United States is one of escalating ambition and technological adaptation. Born out of the energy crises of the 1970s, the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards were established to reduce oil consumption and improve air quality. Initially, these standards brought about significant improvements, forcing automakers to develop more fuel-efficient gasoline engines. However, the path has not been linear, marked by periods of tightening regulations, occasional rollbacks, and constant debate over their economic and environmental impacts.
Early iterations of CAFE standards primarily focused on internal combustion engine vehicles, driving innovations in engine design, aerodynamics, and lightweight materials. As environmental concerns deepened and climate change became a more pressing issue, the focus began to shift. The concept of “fuel efficiency” started to expand beyond just miles per gallon (MPG) to encompass broader emissions reductions, including greenhouse gases. This broadened scope has brought electric vehicles (EVs) and other alternative fuel technologies into the core of the regulatory conversation, fundamentally altering how automakers approach vehicle design and production. The transition signals a move from incremental improvements to a transformational shift towards vehicle electrification and sustainable mobility.
Historical Milestones and Their Impact
Reviewing the past helps contextualize current developments. Major milestones include the initial establishment of CAFE in 1975, subsequent increases during the Obama administration, and the recalibration under the Trump administration. Each phase presented unique challenges and opportunities for the automotive industry.
- 1975 CAFE Standards: Mandated a fleet-wide average of 18 MPG for passenger cars by 1978, rising to 27.5 MPG by 1985, a dramatic increase that spurred initial innovation.
- Obama-Era Increases (2012-2016): Set targets to reach a projected 54.5 MPG for light-duty vehicles by 2025, significantly raising the bar for fuel economy and CO2 emissions.
- Trump-Era Rollbacks (SAFETR): Replaced the ambitious 2025 targets with less stringent requirements, arguing economic strain on manufacturers and consumers, sparking environmental backlash.
These policy shifts highlight the political and economic pressures that constantly bear upon environmental regulations. The ongoing debate typically pits environmental advocates against some industry groups and consumer segments, each presenting compelling arguments about costs, technological feasibility, and societal benefits. Understanding these historical tensions is key to appreciating the current landscape and the complexities surrounding the 2025 standards. The current administration aims to reinstate and even accelerate the aggressive targets, signaling a renewed commitment to environmental protection and the electrification of the automotive fleet.
The Biden Administration’s Approach to 2025 Standards
The Biden administration has made climate change a central pillar of its policy agenda, and federal fuel efficiency standards are a critical tool in achieving ambitious emissions reduction targets. Immediately upon taking office, the administration signaled a clear intent to reverse the previous administration’s rollbacks and accelerate the transition towards a cleaner transportation sector. This involved a multi-agency approach, with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) playing leading roles in proposing stricter regulations.
The core philosophy behind these new proposals is to push the automotive industry further and faster towards electric vehicle adoption while simultaneously improving the efficiency of conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. This dual approach acknowledges that a complete market transformation will take time, but aggressive targets are necessary to meet climate goals. The administration emphasizes the long-term benefits to consumers through reduced fuel costs, improved public health, and enhanced energy security. They also frame these standards as an opportunity for American manufacturers to lead in the global EV market, creating jobs and fostering technological innovation domestically.
Key Proposals and Targets
The primary proposals emanating from the EPA and NHTSA articulate aggressive new targets for corporate average fuel economy and greenhouse gas emissions. These proposals are designed to accelerate the pace set by previous administrations and align the U.S. with other global leaders in emissions reduction.
- EPA’s Proposed Emissions Standards: Aim to achieve a fleet-wide average of 55 MPG for light-duty vehicles by 2026, representing a significant increase from current levels. These regulations consider greenhouse gas emissions directly.
- NHTSA’s Proposed CAFE Standards: Complement the EPA’s proposals by increasing the stringency of traditional fuel economy requirements, pushing for a 40% improvement in fuel efficiency between 2023 and 2026. This would raise the average to approximately 49 MPG by 2026.
- Emphasis on Electric Vehicles: The standards are specifically designed to incentivize the production and adoption of electric vehicles by assigning them zero tailpipe emissions, making it easier for manufacturers to meet overall fleet averages with a higher EV mix.
These ambitious targets are not without their challenges. While environmental groups and EV advocates generally support them, some in the automotive industry express concerns about the speed of the transition, supply chain readiness, and consumer adoption rates. The administration acknowledges these challenges but maintains that the long-term benefits outweigh the short-term hurdles, and that the U.S. has the ingenuity and manufacturing capacity to meet these goals. The integration of EV sales into the compliance calculations is a game-changer, fundamentally shifting the strategic focus of automakers towards electrification.
Technological Advancements Driving Compliance
Meeting stringent federal fuel efficiency standards is not merely a regulatory burden but a powerful catalyst for technological innovation within the automotive industry. Automakers are continuously investing in research and development to create vehicles that are both powerful and remarkably efficient. This drive encompasses a wide range of technologies, from sophisticated internal combustion engine improvements to the rapid evolution of hybrid and electric powertrains. The pressure to comply with escalating targets forces engineers to rethink every component of a vehicle, optimizing for weight, aerodynamics, and energy consumption.
For conventional vehicles, advancements in engine downsizing, turbocharging, direct injection, and advanced transmission systems are key. Lighter materials, such as aluminum and carbon fiber composites, are increasingly used in vehicle construction to reduce overall weight, directly contributing to better fuel economy. Aerodynamic designs are refined through extensive testing to minimize drag. However, the most significant shift is undoubtedly the accelerating pace of electrification, which offers the most direct path to zero tailpipe emissions and thus compliance with the most aggressive standards.
The Role of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles are at the forefront of the strategy for meeting the 2025 federal fuel efficiency standards. Their zero tailpipe emissions mean they are highly weighted in fleet-average calculations, providing a crucial pathway for automakers to comply, even as they continue to sell gasoline-powered vehicles.
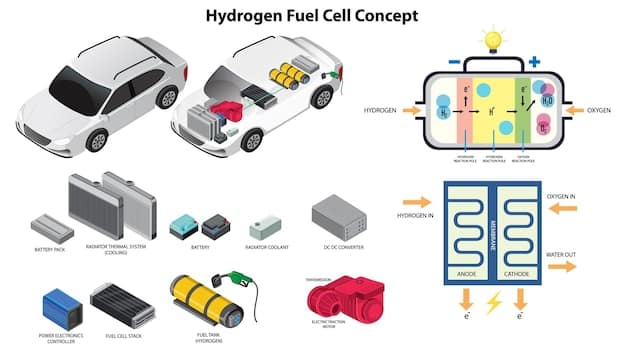
- Regulatory Incentives: The way EVs are factored into CAFE and emissions calculations effectively provides a credit to manufacturers that produce and sell them, making EV production a strategic necessity for compliance.
- Battery Technology: Ongoing research into more energy-dense, faster-charging, and more cost-effective battery chemistries is central to making EVs more appealing and practical for mass adoption. Solid-state batteries are a key area of future development.
- Charging Infrastructure: The widespread availability of charging infrastructure is crucial for consumer confidence in EVs. Both public and private sector investments are accelerating to build robust charging networks.
- Software and Integration: Advanced software managing battery thermal properties, power delivery, and connectivity enhances EV performance and user experience.
The push for EVs is not just about meeting regulations; it represents a fundamental transformation of the automotive industry. Manufacturers are retooling factories, retraining workforces, and forging new supply chain partnerships to support the electric future. This shift is global, with many major automotive markets also setting ambitious electrification targets. The interplay between regulatory pressure and technological advancement is creating a competitive environment where innovation is paramount, promising ever more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles for consumers.
Challenges and Criticisms Facing the New Standards
While the renewed push for stricter fuel efficiency standards is lauded by environmental groups and many policymakers, it is not without its significant challenges and vocal criticisms. Implementing such sweeping changes across an entire industry as complex as automotive raises concerns about economic impact, consumer choice, and the practicalities of a rapid technological transition. Automakers face immense capital investment in retooling production lines for electric vehicles, developing new battery technologies, and training their workforce for a very different manufacturing future. This investment, proponents argue, will pay off in long-term competitiveness, but the short-term strain can be substantial.
Furthermore, critics raise questions about the supply chain for critical raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for EV batteries. Ensuring a stable, ethical, and cost-effective supply of these materials is a global challenge. There are also concerns about the electricity grid’s capacity to handle a massive influx of EV charging, especially during peak demand, and whether the electricity itself will be generated from renewable sources. Without a clean grid, the full environmental benefits of EVs are diminished. These are not minor hurdles but systemic challenges that require coordinated efforts beyond just the automotive sector.
Industry and Consumer Concerns
Both automotive manufacturers and some consumer advocacy groups have voiced reservations about the pace and stringency of the proposed 2025 standards. Their concerns span a range of economic, practical, and market-related issues.
- Cost to Consumers: While EVs offer long-term savings on fuel and maintenance, their initial purchase price is often higher than comparable gasoline vehicles. Critics worry that aggressive standards could force up car prices across the board, making new vehicles less affordable for many consumers.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Despite growing efforts, the charging infrastructure for EVs is still nascent in many regions, creating “range anxiety” and practical barriers for potential buyers. Widespread, reliable, and convenient charging is essential for mass adoption.
- Vehicle Mix and Choice: Some argue that overly stringent standards restrict consumer choice, potentially leading to fewer larger vehicles (like SUVs and trucks, which are popular in the US) that would struggle to meet high efficiency targets with conventional powertrains.
- Job Transition: The shift from internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle production to EV manufacturing requires different skills and processes, raising concerns about potential job displacement in traditional auto manufacturing hubs and the need for significant workforce retraining.
The debate over these standards is complex, balancing environmental imperatives with economic realities and consumer preferences. Proponents argue that the benefits of cleaner air, reduced fuel dependence, and global automotive leadership justify the challenges. Opponents emphasize the potential for unintended negative consequences on affordability and employment. Navigating this tension is central to the ongoing policy discussions and will define the ultimate shape of the 2025 federal fuel efficiency standards.
Implications for Automakers and the Market
The 2025 federal fuel efficiency standards impose significant implications for automakers, effectively reshaping their product development cycles, manufacturing strategies, and overall business models. For companies that have historically relied heavily on gasoline-powered, larger vehicles, the transition is particularly momentous. Meeting the aggressive new targets necessitates a rapid acceleration of electrification strategies. This means not just introducing a few EV models, but planning for entire portfolios dominated by electric vehicles across various segments, from sedans and SUVs to pickup trucks.
The shift impacts everything from inbound logistics for battery components to outbound logistics for charging solutions. Research and development budgets are increasingly skewed towards electric powertrains, software for vehicle performance, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that contribute to overall efficiency. Collaboration and partnerships are also becoming more common, as automakers seek to pool resources for battery development, charging networks, or even platform sharing. The competitive landscape is being fundamentally redrawn, with traditional automakers now competing fiercely with EV-native companies like Tesla, and new players entering the market.
Winners and Losers in a More Efficient Future
The stringent 2025 standards are likely to create clear winners and losers among automotive manufacturers, depending on their agility, investment in new technologies, and strategic foresight.
- Early Adopters and EV Leaders: Companies that have aggressively invested in electric vehicle technology and battery development over the past decade are well-positioned. They have a head start in developing competitive EV models and establishing necessary supply chains. Tesla, for instance, operates at a clear advantage, while companies like General Motors and Ford, with their significant EV investments, are also strong contenders.
- Traditional ICE-Focused Manufacturers: Automakers heavily reliant on traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, especially larger, less efficient models, will face the steepest uphill battle. They will need to rapidly pivot their production and sales strategies, absorbing significant retooling costs and potentially facing compliance penalties if they fail to meet targets.
- Tech Innovators: Companies excelling in software integration, battery management systems, and efficient motor design will gain a significant competitive edge, as these technologies are crucial for maximizing EV performance and range.
- Supply Chain Dynamics: The shift will also impact the broader automotive supply chain. Parts suppliers that specialize in ICE components may struggle, while those focused on EV components (e.g., battery materials, power electronics) will see immense growth.
The market is also likely to see a change in vehicle offerings. While large SUVs and trucks will not disappear, manufacturers will be under immense pressure to electrify these segments to manage their fleet-wide emissions. This implies more hybrid and plug-in hybrid options in the short term, leading to fully electric versions in the mid to long term. Consumer demand will also play a crucial role, with incentives and public perception influencing the speed of EV adoption. The 2025 standards are not just about fuel efficiency; they are about fundamentally transforming the essence of the automotive industry for decades to come.
Consumer Impact and Market Dynamics
The ripple effects of the 2025 federal fuel efficiency standards will inevitably reach the American consumer, influencing everything from vehicle selection and purchase price to long-term ownership costs. On one hand, stricter standards are designed to benefit consumers by reducing fuel consumption, leading to lower operating expenses over the lifetime of a vehicle. This is particularly attractive as fuel prices remain volatile. Consumers can also expect a wider array of more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicle options, including an accelerated introduction of hybrid, plug-in hybrid, and fully electric models across various vehicle segments. The drive for efficiency also pushes manufacturers to innovate in areas like aerodynamics and lightweighting, which can improve overall vehicle performance and handling.
On the other hand, the transition to meet these aggressive standards might present some immediate challenges for consumers. The initial purchase price of new, highly efficient, or electric vehicles could be higher due to the advanced technologies involved and the significant investments automakers are making. While tax credits and incentives might offset some of this cost, accessibility remains a concern for budget-conscious buyers. Furthermore, the evolving charging infrastructure for EVs, while rapidly expanding, may still be a hurdle for some, particularly those in apartments or without reliable home charging options.
Buying Trends and Incentives
The federal standards will undeniably influence consumer buying trends, nudging the market towards more efficient and electric vehicles. Various incentives and market forces will also play a significant role in shaping adoption.

- Increased EV Options: Consumers will see a surge in the availability of electric vehicles, from compact cars to SUVs and even pickup trucks. This expanded choice will make EVs more accessible to a broader demographic.
- Government Incentives: Federal tax credits, as well as state and local incentives, will continue to play a crucial role in making EVs more affordable for buyers, helping to bridge the initial price gap with gasoline cars.
- Rising Fuel Costs: Consistent or rising gasoline prices will make the economic benefits of highly efficient and electric vehicles more apparent, further incentivizing their purchase based on lower running costs.
- Long-Term Savings: Beyond fuel, EVs often have lower maintenance costs dueating fewer moving parts and simpler powertrains, contributing to significant long-term savings for owners.
- Resale Value: As the market shifts, more efficient and electric vehicles may retain a stronger resale value compared to their gasoline counterparts, particularly as new regulations phase in.
Ultimately, the goal of these standards is to provide consumers with better, more sustainable vehicle choices that are also economically advantageous in the long run. The market dynamics will involve a continuous interplay between regulatory pushes, technological advancements, and responsive consumer demand, shaping the future of personal transportation in the United States. While there may be short-term adjustments, the long-term outlook points to a fleet of vehicles that is more efficient, cleaner, and more diversified than ever before.
The Global Context and Future Outlook
The U.S. federal fuel efficiency standards for 2025 do not exist in a vacuum; they are part of a broader global movement towards cleaner transportation and reduced carbon emissions. Many major automotive markets, including the European Union, China, and Japan, have implemented or are proposing their own stringent emissions and fuel economy regulations, often even more aggressive than those in the U.S. This global convergence means that automakers are designing vehicles for a world where efficiency and electrification are paramount, rather than just for a single market. This creates a powerful shared incentive for innovation, as companies can leverage economies of scale in developing common platforms and technologies for multiple regions.
The global context also highlights the geopolitical implications of the automotive transition. Countries are vying for leadership in EV manufacturing, battery production, and critical mineral supply chains, recognizing the immense economic and strategic importance of these new industries. The U.S. standards, therefore, are not just about domestic environmental policy but also about ensuring American competitiveness in the future of mobility. The future outlook suggests a continued tightening of regulations, an acceleration of EV adoption, and further integration of renewable energy into the transportation sector.
Beyond 2025: What Comes Next?
The 2025 standards are a significant milestone, but they are by no means the final destination. The trajectory of federal policy points to even more ambitious goals in the years beyond.
- Continued Stringency: Expect ongoing increases in fuel efficiency and emissions standards beyond 2025, pushing for near-zero emissions from the vehicle fleet ultimately.
- Focus on Lifecycle Emissions: Future regulations may increasingly consider the full lifecycle emissions of vehicles, including manufacturing processes and the energy sources used to generate electricity for EVs, not just tailpipe emissions.
- Advanced Technologies: Further development in battery technology, hydrogen fuel cells, and even synthetic fuels for existing ICE vehicles could play a role in achieving ultimate climate goals.
- Integrated Policy: Greater integration between transportation policy and energy policy will be critical, ensuring sufficient renewable energy generation to power an electrified fleet.
- Autonomous Vehicles: While not directly tied to fuel efficiency, the rise of autonomous vehicles could indirectly impact energy consumption through optimized routing and platooning, leading to further reductions.
The journey towards a truly sustainable transportation system is complex and multifaceted, requiring continuous innovation, adaptive policy, and global cooperation. The 2025 federal fuel efficiency standards represent a crucial step on this path, setting the stage for a future where vehicles are not only more efficient but also environmentally responsible throughout their entire lifecycle. The automotive industry is in the midst of its most profound transformation in a century, driven by a combination of regulatory imperatives, technological breakthroughs, and a growing societal demand for sustainable solutions.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🎯 Biden’s Vision | Administration aims for aggressive targets, accelerating EV transition to meet climate goals. |
| ⚡ EV Focus | Electric vehicles are crucial for compliance, heavily incentivized in fleet calculations. |
| ⚖️ Challenges | Concerns include vehicle cost, charging infrastructure, and supply chain readiness. |
| 🌍 Global Impact | US standards align with international trends, fostering global auto industry transformation. |
Answers to Your Questions About 2025 Federal Fuel Efficiency Standards
The primary goals are to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, decrease U.S. reliance on fossil fuels, and push the automotive industry towards greater adoption of electric vehicles. These standards aim to mitigate climate change impacts, improve air quality, and secure America’s position in the global clean energy economy. They also intend to save consumers money on fuel costs over time.
These standards will accelerate the introduction of more fuel-efficient and electric vehicle models across various segments. Consumers can expect a broader range of hybrids, plug-in hybrids, and fully electric cars, including SUVs and trucks, as manufacturers strive to meet fleet-wide averages. This shift offers more choice for drivers seeking lower emissions and reduced running costs.
While the advanced technologies required by the new standards may initially increase manufacturing costs, potentially leading to higher sticker prices for some vehicles, proponents argue these costs are often offset by significant long-term fuel savings and government incentives like tax credits. The aim is to balance initial expenditure with lifetime economic benefits for the consumer.
Electric vehicles (EVs) are central to meeting the 2025 standards. Due to their zero tailpipe emissions, they receive favorable treatment in fleet-average calculations, making them crucial for automakers to achieve compliance. The standards are specifically designed to incentivize greater EV production and sales, accelerating the transition from gasoline to electric powertrains across the market.
Main criticisms include concerns about the potential for higher new vehicle prices, a rapid transition pace straining manufacturing capabilities, and challenges with scaling up charging infrastructure. Some also worry about limiting consumer choice, particularly for larger vehicles, and geopolitical issues related to securing raw materials for battery production, sparking ongoing debate.
Conclusion
The 2025 federal fuel efficiency standards mark a pivotal moment in the evolution of the automotive industry and environmental policy in the United States. Driven by the Biden administration’s commitment to climate action, these regulations are designed to accelerate the transition towards a cleaner, more sustainable transportation sector. While they undoubtedly present significant challenges for automakers—requiring massive investments in electric vehicle technology, retooling of production lines, and re-evaluation of supply chains—they also serve as a powerful catalyst for innovation. For consumers, the standards promise a wider array of more efficient and electric vehicle options, leading to long-term savings on fuel costs and contributing to cleaner air. As the global automotive landscape rapidly shifts towards electrification, these U.S. standards are not just about domestic policy; they are about ensuring American competitiveness and leadership in the future of mobility. The path ahead will require careful navigation of economic realities and technological advancements, but the direction is clear: a more efficient, electric, and environmentally responsible automotive future.





