2025 EV Home Charging: Save $500 Annually on Fuel Costs
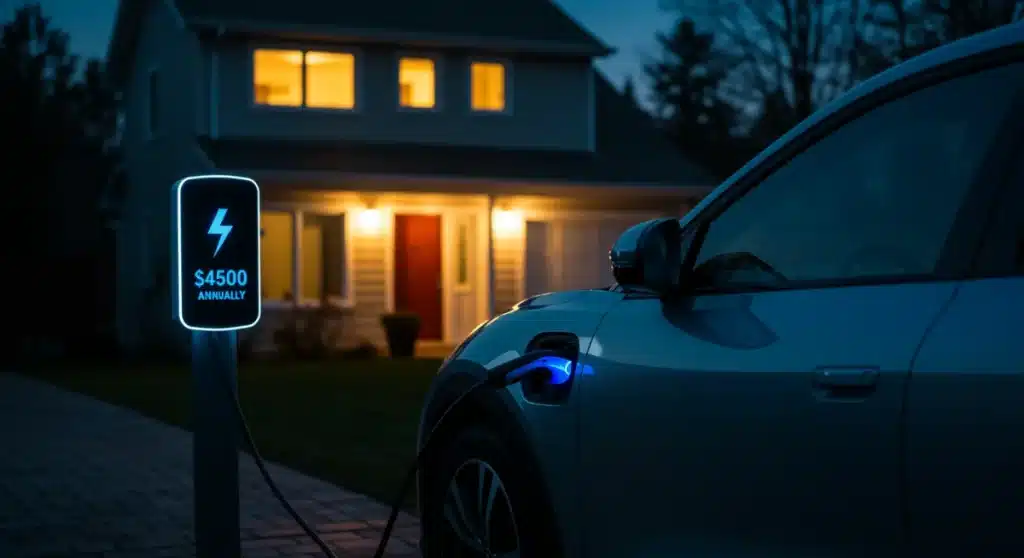

As 2025 approaches, a significant financial shift is underway for American drivers. New projections indicate that utilizing EV home charging savings could lead to annual fuel cost reductions of up to $500 for households across the United States. This development marks a pivotal moment for electric vehicle adoption and personal finance.
The Economic Shift: Fuel Savings Take Center Stage
The economic landscape for vehicle ownership is rapidly evolving, with electric vehicles (EVs) at the forefront of this transformation. As gasoline prices continue to fluctuate, the stability and lower cost of electricity for vehicle charging are becoming increasingly attractive to consumers nationwide. This shift is particularly pronounced when considering home charging solutions.
Recent analyses, including reports from the U.S. Department of Energy and independent energy consultancies, project substantial savings for EV owners who primarily charge their vehicles at home. These savings are not merely theoretical; they represent tangible financial benefits that directly impact household budgets, making EV ownership more accessible and appealing to a broader demographic. The convenience of overnight charging eliminates frequent trips to gas stations, further enhancing the appeal.
Understanding the Cost Differential
The primary driver of these savings is the significant cost differential between gasoline and electricity. While there are regional variations in electricity rates, the per-mile cost of powering an EV at home is consistently lower than that of gasoline for an internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle. This economic advantage is a key factor in the growing popularity of EVs.
- Lower Per-Mile Cost: Electricity is generally cheaper per mile than gasoline.
- Off-Peak Charging: Many utility providers offer lower rates during off-peak hours, maximizing savings for home chargers.
- Reduced Maintenance: EVs typically require less maintenance than ICE vehicles, adding to overall savings.
The 2025 Outlook: Up to $500 Annually
By 2025, the financial impact of EV home charging is expected to solidify, with projections showing average annual fuel cost savings reaching up to $500 for many U.S. households. This figure is based on typical driving habits, average electricity rates, and projected gasoline prices. The consistency of these savings provides a strong incentive for consumers to make the switch to electric.
This estimated saving is not uniform across all states or all driving patterns. Factors such as local electricity rates, the efficiency of the EV, and the total miles driven annually all play a role. However, the overarching trend indicates a clear financial advantage, positioning home charging as a cornerstone of cost-effective EV ownership. The accessibility of charging infrastructure at home also reduces range anxiety, a common concern among potential EV buyers.
Factors Influencing Savings
Several variables contribute to the potential for significant savings. Understanding these factors can help consumers optimize their charging habits and maximize their financial benefits.
- Electricity Rates: Regional differences in utility rates can impact overall savings.
- Charging Habits: Utilizing off-peak hours for charging can significantly reduce costs.
- Vehicle Efficiency: More efficient EV models will naturally incur lower charging costs.
Infrastructure Growth and Accessibility
The expansion of home charging infrastructure is critical to realizing these projected savings. As EV adoption increases, so too does the demand for convenient and efficient home charging solutions. Manufacturers and utility companies are responding to this demand by offering a wider range of charging equipment and programs.
The availability of Level 2 chargers, which provide faster charging speeds than standard household outlets, is becoming more widespread and affordable. Furthermore, government incentives and rebates for charger installation continue to make home charging more accessible for many homeowners. This growing ecosystem of support is vital for sustaining the momentum of EV adoption and ensuring that the financial benefits are widely distributed.
Government Incentives and Programs
Federal and state governments are actively promoting EV adoption through various incentives, including tax credits for purchasing EVs and installing home charging equipment. These programs aim to reduce the initial financial barrier to entry, making the long-term savings more achievable for a broader segment of the population.
- Federal Tax Credits: Available for eligible EV purchases and charging equipment.
- State and Local Rebates: Many states offer additional incentives for EV buyers and charger installations.
- Utility Programs: Some utilities provide discounts or special rates for EV owners.
Beyond Fuel: Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
While fuel savings are a major component of the financial benefits of EV home charging, it is essential to consider the broader total cost of ownership (TCO). EVs often have lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts and the absence of oil changes. This contributes to even greater long-term financial advantages for owners.
The initial purchase price of an EV can sometimes be higher than a comparable gasoline vehicle, but when factoring in fuel savings, maintenance reductions, and potential tax credits, the TCO for an EV often becomes more favorable over its lifespan. This holistic view of vehicle expenses underscores the growing economic viability of electric transportation. Insurance costs for EVs are also becoming more competitive as the market matures.
Maintenance Advantages of EVs
Electric vehicles benefit from a simpler powertrain, which translates into fewer components that require regular maintenance or replacement. This inherent design advantage significantly reduces the frequency and cost of service appointments.
- No Oil Changes: Eliminates a recurring maintenance expense.
- Fewer Moving Parts: Reduces wear and tear on mechanical components.
- Brake Regeneration: Extends the life of brake pads and rotors.
Regional Variations and Maximizing Savings
The potential for EV home charging savings varies significantly across different regions of the United States. States with lower electricity rates and higher gasoline prices naturally offer greater financial incentives for EV adoption. Conversely, areas with higher electricity costs may see slightly smaller, though still substantial, savings.
Consumers can maximize their savings by understanding their local electricity tariffs and strategically planning their charging times. Many utility providers offer time-of-use (TOU) rates, which allow EV owners to charge during off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper. Smart charging technologies can automate this process, ensuring vehicles are charged efficiently and cost-effectively, further enhancing the financial benefits. Understanding these regional nuances is key to optimizing EV ownership.
Strategies for Cost-Effective Charging
Adopting smart charging practices can significantly enhance the financial benefits of owning an EV. These strategies are designed to leverage off-peak electricity rates and efficient energy use.
- Time-of-Use (TOU) Plans: Charge during designated off-peak hours for lower rates.
- Smart Chargers: Utilize chargers with scheduling features to automate off-peak charging.
- Solar Integration: Combine home charging with rooftop solar panels for even greater energy independence and savings.
Environmental and Societal Impact
Beyond the personal financial benefits, the widespread adoption of EV home charging savings has profound environmental and societal implications. Reducing reliance on fossil fuels through EV use contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions, improving air quality and combating climate change. This shift supports national and global sustainability goals.
The increased demand for electricity also drives innovation in renewable energy sources, as utilities seek cleaner and more sustainable ways to power the grid. Furthermore, a decentralized charging network, largely powered by home charging, enhances energy resilience and reduces strain on public charging infrastructure, fostering a more robust and sustainable transportation ecosystem for the future.
Broader Benefits of EV Adoption
The transition to electric vehicles offers a multitude of advantages that extend far beyond individual financial savings, impacting communities and the environment positively.
- Reduced Emissions: Contributes to cleaner air and a healthier environment.
- Energy Independence: Less reliance on imported fossil fuels strengthens national energy security.
- Quieter Communities: EVs produce less noise pollution than traditional gasoline cars.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Annual Fuel Savings | US households can save up to $500 annually on fuel costs by 2025 with EV home charging. |
| Cost Differential | Electricity is consistently cheaper per mile than gasoline, driving significant economic benefits. |
| Infrastructure & Incentives | Growing home charging infrastructure and government incentives make EV adoption more accessible. |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Lower maintenance costs further enhance the long-term financial advantages of EVs. |
Frequently Asked Questions About EV Home Charging Savings
By 2025, many U.S. households can expect to save up to $500 annually on fuel costs by primarily charging their electric vehicles at home. This figure varies based on local electricity rates, driving habits, and the specific EV model’s efficiency, but represents a significant financial advantage.
Yes, federal tax credits are often available for eligible home EV charging equipment and installation costs. Many states and local utility companies also offer additional rebates or programs to encourage the adoption of home charging infrastructure, further reducing upfront expenses.
To maximize savings, consider charging during off-peak hours if your utility offers time-of-use rates. Using a smart charger to schedule charging automatically can help. Additionally, maintaining your EV for optimal efficiency and exploring local utility programs can further reduce costs.
While the upfront cost of an EV and charger can be higher, the long-term savings on fuel and reduced maintenance often make it a worthwhile investment. When factoring in federal and state incentives, the total cost of ownership over an EV’s lifespan is increasingly competitive.
Home EV charging dramatically reduces reliance on fossil fuels, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality. This shift supports environmental sustainability goals and contributes to a cleaner, healthier planet by minimizing the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
What Happens Next
The projected financial impact of EV home charging savings by 2025 signifies a clear trajectory for the automotive industry and consumer behavior. As these savings become more widely recognized and accessible, expect a continued acceleration in EV adoption across the U.S. Policymakers and utility providers will likely introduce further incentives and infrastructure enhancements to support this growth. Consumers should monitor local energy markets and government programs to fully capitalize on these evolving financial benefits. The transition to electric vehicles is not just an environmental imperative but a growing economic advantage for American households.